CANCER: DEMYSTIFYING THE MENACE 1
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Well, today is cancer day and I thought it wise to bring to you guys a lay-mans summary of cancer; something that explains it in terms you guys would be able to relate easier to. Here you go:
Defining Cancer
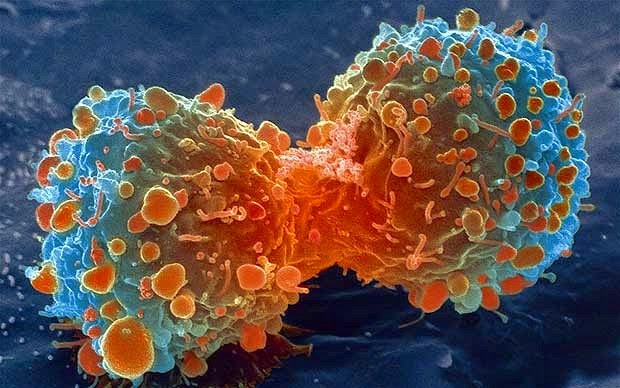
Cancer is a term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and are able to invade other tissues. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems.
Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. There are more than 100 different types of cancer. Most cancers are named for the organ or type of cell in which they start – for example, cancer that begins in the colon is called colon cancer; cancer that begins inmelanocytesof the skin is called melanoma.
Cancer types can be grouped into broader categories. The main categories of cancer include:
- Carcinoma– cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs. There are a number of subtypes of carcinoma, includingadenocarcinoma,basal cell carcinoma,squamous cell carcinoma, andtransitional cellcarcinoma.
- Sarcoma– cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue.
- Leukemia– cancer that starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood.
- Lymphoma and myeloma– cancers that begin in the cells of theimmune system.
- Central nervous system cancers– cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
Cancers are often referred to by terms that contain a prefix related to the cell type in which the cancer originated and a suffix such as -sarcoma, -carcinoma, or just -oma. Common prefixes include:
- Adeno- = gland
- Chondro- = cartilage
- Erythro- = red blood cell
- Hemangio- = blood vessels
- Hepato- = liver
- Lipo- = fat
- Lympho- = white blood cell
- Melano- = pigment cell
- Myelo- = bone marrow
- Myo- = muscle
- Osteo- = bone
- Uro- = bladder
- Retino- = eye
- Neuro- = brain
Origins of Cancer
All cancers begin in cells, the body’s basic unit of life. To understand cancer, it’s helpful to know what happens when normal cells become cancer cells.
The body is made up of many types of cells. These cells grow and divide in a controlled way to produce more cells as they are needed to keep the body healthy. When cells become old or damaged, they die and are replaced with new cells.
However, sometimes this orderly process goes wrong. The genetic material (DNA) of a cell can become damaged or changed, producingmutationsthat affect normal cell growth and division. When this happens, cells do not die when they should and new cells form when the body does not need them. The extra cells may form a mass of tissue called atumor.
(Image from Understanding Cancer Series: Cancer.)
Not all tumors are cancerous; tumors can be benign or malignant.
- Benign tumorsaren’t cancerous. They can often be removed, and, in most cases, they do not come back. Cells in benign tumors do not spread to other parts of the body.
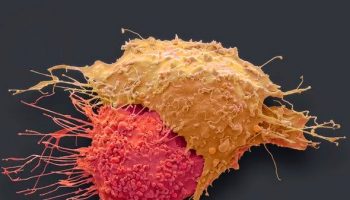
- Malignant tumorsare cancerous. Cells in these tumors can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. The spread of cancer from one part of the body to another is called metastasis.
Some cancers do not form tumors. For example, leukemia is a cancer of the bone marrow and blood.
What are the symptoms of cancer?
Cancer symptoms are quite varied and depend on where the cancer is located, where it has spread, and how big the tumor is. Some cancers can be felt or seen through the skin – a lump on the breast or testicle can be an indicator of cancer in those locations. Skin cancer (melanoma) is often noted by a change in a wart or mole on the skin. Some oral cancers present white patches inside the mouth or white spots on the tongue.
Other cancers have symptoms that are less physically apparent. Some brain tumors tend to present symptoms early in the disease as they affect important cognitive functions. Pancreas cancers are usually too small to cause symptoms until they cause pain by pushing against nearby nerves or interfere with liver function to cause a yellowing of the skin and eyes called jaundice. Symptoms also can be created as a tumor grows and pushes against organs and blood vessels. For example, colon cancers lead to symptoms such as constipation, diarrhea, and changes in stool size. Bladder or prostate cancers cause changes in bladder function such as more frequent or infrequent urination.
As cancer cells use the body’s energy and interfere with normal hormone function, it is possible to present symptoms such as fever, fatigue, excessive sweating, anemia, and unexplained weight loss. However, these symptoms are common in several other maladies as well. For example, coughing and hoarseness can point to lung or throat cancer as well as several other conditions.
When cancer spreads, or metastasizes, additional symptoms can present themselves in the newly affected area. Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes are common and likely to be present early. If cancer spreads to the brain, patients may experience vertigo, headaches, or seizures. Spreading to the lungs may cause coughing and shortness of breath. In addition, the liver may become enlarged and cause jaundice and bones can become painful, brittle, and break easily. Symptoms of metastasis ultimately depend on the location to which the cancer has spread.
How cancer spreads–
scientists reported inNature Communications(October 2012 issue) that they havediscovered an important clue as to why cancer cells spread. It has something to do with their adhesion (stickiness) properties. Certain molecular interactions between cells and the scaffolding that holds them in place (extracellular matrix) cause them to become unstuck at the original tumor site, they become dislodged, move on and then reattach themselves at a new site.
The researchers say this discovery is important because cancer mortality is mainly due to metastatic tumors, those that grow from cells that have traveled from their original site to another part of the body. Only 10% of cancer deaths are caused by the primary tumors.
The scientists, from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, say that finding a way to stop cancer cells from sticking to new sites could interfere with metastatic disease, and halt the growth of secondary tumors.
How is cancer diagnosed and staged?
Early detection of cancer can greatly improve the odds of successful treatment and survival. Physicians use information from symptoms and several other procedures to diagnose cancer. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, PET scans, and ultrasound scans are used regularly in order to detect where a tumor is located and what organs may be affected by it. Doctors may also conduct an endoscopy, which is a procedure that uses a thin tube with a camera and light at one end, to look for abnormalities inside the body.

Extracting cancer cells and looking at them under a microscope is the only absolute way to diagnose cancer. This procedure is called a biopsy. Other types of molecular diagnostic tests are frequently employed as well. Physicians will analyze your body’s sugars, fats, proteins, and DNA at the molecular level. For example, cancerous prostate cells release a higher level of a chemical called PSA (prostate-specific antigen) into the bloodstream that can be detected by a blood test. Molecular diagnostics, biopsies, and imaging techniques are all used together to diagnose cancer.
After a diagnosis is made, doctors find out how far the cancer has spread and determine the stage of the cancer. The stage determines which choices will be available for treatment and informs prognoses. The most common cancer staging method is called the TNM system. T (1-4) indicates the size and direct extent of the primary tumor, N (0-3) indicates the degree to which the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, and M (0-1) indicates whether the cancer has metastasized to other organs in the body. A small tumor that has not spread to lymph nodes or distant organs may be staged as (T1, N0, M0), for example.
TNM descriptions then lead to a simpler categorization of stages, from 0 to 4, where lower numbers indicate that the cancer has spread less. While most Stage 1 tumors are curable, most Stage 4 tumors are inoperable or untreatable.
How is cancer treated?
Cancer treatment depends on the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer (how much it has spread), age, health status, and additional personal characteristics. There is no single treatment for cancer, and patients often receive a combination of therapies and palliative care. Treatments usually fall into one of the following categories: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, or gene therapy.
previous article
FLUSH THE EXTRA WEIGHT
next article
PEPTIC ULCER: LATEST DEVELOPMENTS
The author Prince
Hi, I’m Prince.. a registered Dietitian, an avid reader and a passionate writer. I hope you enjoy my articles as much as I enjoy writing them