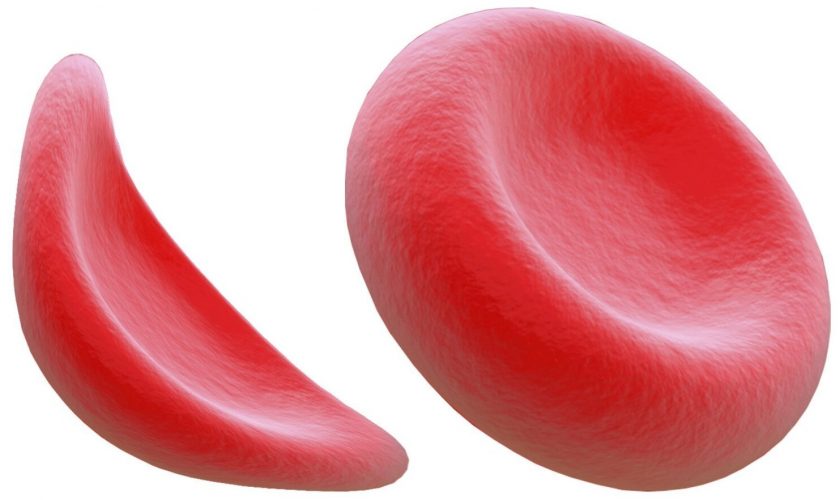
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder where red blood cells that carry oxygen assume a totally different shape from the normal. Normally, red blood cells assume a disc shape while flowing through blood vessels, but in sickle cell anemia, red blood cells assume a crescent like shape.
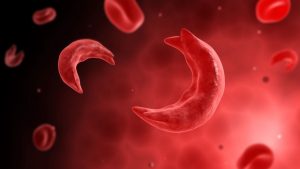
Devastating as the disease might be, no cure has been found yet.
Interestingly, through research and a bid to increase knowledge, it has been found out that nutritional problems are fundamental to the severity of the disease, thereby increasing interests to promote dietary supplementation for decreasing morbidity and to help improve the quality of patient’s life.
Several methods of treatment and management have been in use for quite a while now and they include:
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
-Hydroxycarbamide (or hydroxyurea) This substance helps to reduce the number of painful episodes in Hbss patients.
-Blood transfusion: A number of observational and randomised controlled trials have established the pivotal role of transfusion therapy in the management of SCD, most notably in primary stroke prevention.
-Allogeneic HSCT and gene therapy: Allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is the only curative treatment for SCD and is successful in 85%–90% of patients. Transplantation offers disease-free survival and stabilisation of neurological lesions.
Features as growth retardation, impaired immune function, and delayed menarche do suggest a relationship between sickle cell disease and undernutrition. Also, a variety of micronutrient deficiency has been suggested in sickle cell disease.
– Several reports indicate that vitamin E levels are low in sickle erythrocytes. Since these abnormal red cells both generate excessive oxidation products and are more sensitive to oxidant stress, supplementation with vitamin E is advised in people with sickle cell anaemia.
– Complications of sickle cell disease as poor ulcer healing, growth retardation, delays in sexual development, immune deficiencies have been linked to zinc deficiency. It is also pertinent that zinc be supplemented in people with sickle cell.
– Deficiency of Vitamin D is common in sickle cell disease due to dark skin pigmentation, limited sun exposure, increased catabolism and decreased nutrient and energy intake. Vitamin D in it’s entirety is crucial for calcium homeostasis and essential for bone mineralization.
Therefore, a high dose of 100,000 International units (IU) (equivalent to 3,333 IU/day) versus the standard treatment 12,000 IU (equivalent to 400 IU/day) of oral vitamin D3 supplements might just help in reducing risk of respiratory infections.
– Amino acids like arginine and glutamine also play important roles in the synthesis of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide makes it possible for easy blood flow by dilating the blood vessels properly. Increased deficiency of the duo might lead to metabolic stress, increased resting energy expenditure (REE), muscle wasting and decreased immune function. Supplementing with 600mg/kg/day of glutamine showed improved nutritional status of glutamine.
EMERGING INTERVENTIONS
Recently, derivatives from plants has been studied to show their effects in treating people with SCD. Some plants which contain peculiar antioxidants are being studied and there might just be hope to managing SCD.
Exploration of extracts from Moringa oleifera (Moringa), Cajanus cajan (pigeon pea) , Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloides (artar root), and Carica papaya (paw paw) are all being studied to see their possible effects in treating oxidative stress in SCD patients.
With these ongoing experiments, it has been noticed that extracts from these plants could aid in the resistance of hemolysis and reduce the number of sickled red blood cells.
Also, it has been noticed that exercise might play an important role in SCD patients. Exercise helps in reducing oxidative stress and also in the release of nitric oxide which helps in the proper flow of blood through vessels.
CONCLUSION
The nutritional risks faced by SCD patients are usually high and mostly unnoticed. Its imperative to include nutrition as an adjuvant therapy for addressing chronic diseases related with SCD in order to aid effective management.
SOURCES: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3551592/
https://www.dovepress.com/nutrition-in-sickle-cell-disease-recent-insights-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-NDS
https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/sickle-cell-anemia-a-to-z
https://adc.bmj.com/content/100/1/48
https://www.todaysdietitian.com/news/042412_news.shtml

