Normally, everyone is more concerned about losing weight, so more attention is given to them than those that wants to gain weight. And it also seems like those who wants to gain weight has been neglected by all.
So lets see some reasons why you might not be adding weight adequately and lets also see if there are implications with low weight.
1. WRONG CHOICE OF FOODS: for some people, high fatty foods would help them gain weight, so they jump on deep fried foods, ice creams, junks, chocolates etc. These foods might contain trans fats which might even be very detrimental to you health. So instead of making you add weight adequately, they might just get your stomach bulged.
Foods to include in your diet to help gain weight: nuts, milk, fatty fruits like avocado, energy dense fruits like banana, apples, coconut etc.
2. HYPERTHYROIDISM: this happens when your thyroids become so overactive. The thyroid glands are responsible for controlling metabolism (especially for weight gain and loss) in the body. When they are overactive, it means that energy from food is broken so fast, thereby making it hard for the body to utilize energy. You will need extra hands to achieve weight gain if you are on this table. A dietitians place cannot be overemphasized
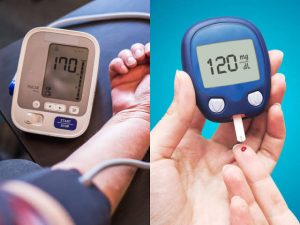
3. TYPE 1 DIABETES: In type 1 diabetes, the cells that produce insulin are totally destroyed leading to a spike in blood glucose. Wen type 1 diabetes is left unmanaged for a long while, it could lead to excess glucose flowing in the blood; the body has to excrete this excess glucose through the urine. When this happens constantly, unintentional weight loss sets in
4. INFLAMMATORY DISEASES: This is the umbrella term for anything disorder that affects the small intestine especially. These disorders most times comes with diarrhea, and this automatically leads to unintentional weight loss
In all of this, it is important to work with a dietitian so they can address whatever underlying issue is the reason for your unintentional weight loss. Addressing them with drugs alone or just eating anything that comes your way wont give a reasonable result.
SOURCES:
– https://www.healthline.com/health/why-cant-i-gain-weight
https://www.healthline.com/health/hyperthyroidism
– https://thegeriatricdietitian.com/why-am-i-not-gaining-weight/