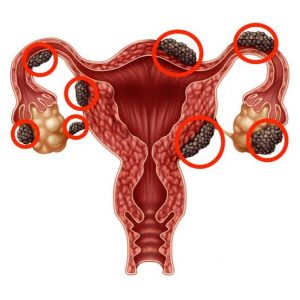
Endometriosis occurs when non-cancerous tissues that resemble the ones lining your uterus , begin to grow outside of the uterus in places like the ovaries, the fallopian tube, pelvis and bowel.
It is a hormone dependent type of condition (especially steroid based hormone estrogen).
The tissues in the uterus becomes thicker than normal, breaks down and leave the body during menstruation, but these tissues that grow outside of the uterus also thicken and break down but cant leave the body thereby leading to pain, inflammation, formation of scar tissue and most likely, potential fertility problems.
According to a study, about 70 million women all over the world are affected by endometriosis. Surprisingly, the disease is even more common than breast cancer and diabetes.
Endometriosis usually occurs during active menstruation when there is still much release of estrogen (i.e it is hormone dependent), it rarely occurs after menstruation.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Symptoms always vary from one woman to another, might come in as mild or moderate or severe.
The degree of pain doesn’t always equate the severity of the condition; you might have very excruciating pains and it’s a mild condition.
Symptoms involved in endometriosis include:
- excruciating pains during period
- pain experienced in the lower abdomen and back either before or during menstruation
- cramps around menstruation week
- heavy bleeding
- infertility problems
- pain after sexual intercourse
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating
WHAT EXACTLY CAUSES ENDOMETRIOSIS?
The etiology behind endometriosis is not known yet, but according to some theories put forward, these suggested causes might be linked to the condition:
- Genetics: the condition most likely runs in families and affects people of some ethnic groups more
- Retrograde menstruation: this happens when some of the womb lining flows up back through the fallopian tubes and hangs on to some organs of the pelvis instead of leaving the body as period.
- When the immune system is malfunctioning
These suggested theories don’t fully explain the causes of endometriosis; it is a condition caused by many factors put together.
RISK FACTORS
Some other factors include:
- AGE: usually affects women from the ages of 25-40, symptoms can be seen from puberty though.
- FAMILY HISTORY
- PREGNANCY HISTORY: pregnancy might have the tendency of decreasing the risk of endometriosis, those who haven’t had children might have higher risks of endometriosis.
- MENSTRUATION HISTORY: issues associated with this can include shorter cycles, heavier and longer periods and might place the individual at higher risks.
HOW CAN I PREVENT ENDOMETRIOSIS?
Sadly, there is no known way to prevent endometriosis. The possible ways are to create awareness, ensure early diagnosis and management to help slow down or halt the natural progression of the disease.
HOW IS IT DIAGNOSED?
Endometriosis can be suspected from history; tender masses might be visible on the vagina and cervix during pelvic examination.
TREATMENT OPTIONS
Even though there is no known treatment option for endometriosis, it can be managed to help reduce symptoms. Possible ways to help manage endometriosis includes:
- nutritional therapy
- exercise
- pain medication
- hormone therapy
- surgery
These options totally depend on the severity of the condition.
HOW ENDOMETRIOSIS MAY BE LINKED TO DIET
Diet may have a potential role in the cause of endometriosis through its influence on hormones derived from cholesterol. Hormones like oestrogen which are cholesterol based are the major culprit in endometriosis. So, studies have shown that a plant-based and high fibre diet increase oestrogen secretion and reduce the availability of oestrogen, and this might help reduce endometriosis progression. This diet would help to modify the risk of endometriosis by altering the metabolism of cholesterol based hormones.
FOODS THAT MAY NEGATIVELY AFFECT ENDOMETRIOSIS
Endometriosis can be influenced by your lifestyle, and this determines the severity of the condition and the pain experienced.
The following factors might negatively influence the condition:
- High intake of transfat : research has it that women who consumed high amounts of transfat especially from fried and processed foods had a higher rate of diagnoses.
- Red meat consumption
- Gluten: A study showed that most women experienced a decreased pain while they went on a gluten free diet
- High FODMAP diet: low FODMAP diets are majorly prescribed to people who has irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A research found out that those with IBS and endometriosis that followed a low FODMAP diet had reduced symptoms
Alcohol, caffeine, gluten, red meat, saturated and trans fat can negatively affect hormone regulation in people with endometriosis as they lead to progression of the disorder. So, they should be totally avoided
FOODS THAT MAY POSITIVELY AFFECT ENDOMETRIOSIS
A nutrient dense and well adequate diet can help to reduce symptoms from endometriosis. you should consider:
- A high fibre diet: a diet high in fibre helps reduce the production of oestrogen which is implicated in the mechanism of endometriosis, and also helps to reduce insulin production, which relates to the progression of endometriosis. foods high in fibre includes green leafy vegetables, legumes and whole grains.
- iron-rich foods, such as dark leafy greens, broccoli, beans, fortified grains, nuts, and seeds
- foods rich in essential fatty acids, such as salmon, sardines, walnuts, chia, and flax seeds
- antioxidant-rich foods found in colorful fruits and vegetables, such as oranges, berries, dark chocolate, spinach, and beets. Studies has linked oxidative stress to the progression of the disease, so its important to also consider these antioxidant rich food sources.
SUPPLEMENTS ALSO HAVE A ROLE TO PLAY
Apart from an adequate diet, nutritional supplements also have unique roles to play while managing endometriosis.
For example, supplementing with 1200 IU of vitamin E and 1000 IU of vitamin C was shown to reduce pelvic pain in some women with endometriosis after a clinical trial.
Also, curcumin, vitamins A and D proved to help in the management of endometriosis
EXERCISE AND OTHER ALTERNATIVES
Exercise could help to manage endometriosis as it reduces the production of estrogen and helps in the release of serotonin “the feel good hormone”. Some relaxation techniques can be explored
- meditation
- yoga
- accupunture
- massage
SUMMARY
Lifestyle changes and dietary patterns could help to reduce the symptoms associated with endometriosis, you can speak to a dietitian and a doctor to help you through this condition as everyone’s body’s are different and should be handled individually.
SOURCES
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3941414/
- https://nutritionguide.pcrm.org/nutritionguide/view/Nutrition_Guide_for_Clinicians/1342065/all/Endometriosis
- Zondervan KT, Becker CM, Missmer SA. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med 2020; 382:1244-56.
- Agarwal SK, Chapron C, Giudice LC, et al. Clinical diagnosis of endometriosis: a call to action. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2019(4):354-64.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/247770015_Diet_-_A_New_Approach_To_Treating_Endometriosis_-_What_Is_The_Evidence
- Harris, H. R., Chavarro, J. E., Malspeis, S., Willett, W. C., & Missmer, S. A. (2013). Dairy-food, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D intake and endometriosis: a prospective cohort study. American Journal Of Epidemiology, 177(5), 420-430.
- Missmer, S. A., Chavarro, J. E., Malspeis, S., Bertone-Johnson, E. R., Hornstein, M. D., Spiegelman, D., Hankinson, S. E. (2010).
- A prospective study of dietary fat consumption and endometriosis risk. Hum Reprod, 25(6), 1528-1535.


 Generally, one major factor considered to affect fertility is age. As you grow older, your organs, hormones and system seem to deteriorate.
Generally, one major factor considered to affect fertility is age. As you grow older, your organs, hormones and system seem to deteriorate.