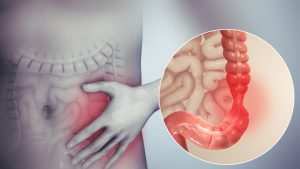
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most common functional bowel disorders.
Between 1 in 11 people and 1 in 26 people globally experience irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms.
The condition affects more women than men. Some people with IBS have minor symptoms. However, for others the symptoms are significant and disrupt daily life.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common condition that affects the digestive system.
It causes symptoms like stomach cramps, bloating, diarrhoea and constipation. These tend to come and go over time, and can last for days, weeks or months at a time.It’s usually a lifelong problem
IBS could also be termed as a disorder of gut-brain interaction, meaning it falls within the realm of the growing field of neurogastroenterology and can be understood through an interdisciplinary biopsychosocial model, which looks at the interconnection between biology, psychology, and socio-environmental factors
In simple terms, there is a relationship between mental stress and the digestive system.
It is mostly associated with a change in stool frequency, stool form, and/or relief or worsening of abdominal pain related to defecation.
Unlike other GI disorders, there are no scarring or lesions in the tract of someone with IBS.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR?
Symptoms are almost same with other GI diseases and they include:
– Cramping
– abdominal pain
– bloating and gas
– constipation
– Diarrhea
You might be wondering how one can be constipated and still have issues with diarrhea. It is very common for people with IBS to have episodes of both constipation and diarrhea.
Symptoms such as bloating and gas typically go away after you have a bowel movement.
Symptoms of IBS aren’t always persistent. They can resolve, only to come back. However, some people do have continuous symptoms.
Women tend to have symptoms around their periods but reduced symptoms in men. Men have same symptoms as women but tend to report it less.
DIAGNOSIS
Your doctor may be able to diagnose IBS based on your symptoms. They may also take one or more of the following steps to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms:
– Suggest that you adopt a certain diet or cut out specific food groups for a period to rule out any food allergies
– Suggest a stool sample examined to rule out infection
– Suggest blood tests to check for anemia and rule out celiac disease
– Perform a colonoscopy
WHAT COULD BE THE CAUSE(S)
Although there are many ways to treat IBS, the exact cause of IBS is unknown
The varied possible causes make IBS difficult to prevent.
The physical processes involved in IBS can also vary, but may consist of:
– slowed or spastic movements of the colon, causing painful cramping
– abnormal serotonin levels in the colon, affecting motility and bowel movements
– mild celiac disease that damages the intestines, causing IBS symptoms
IS THERE ANY TREATMENT OPTION?
There is no cure for IBS. Treatment is aimed at symptom relief. Initially, your doctor may have you make certain lifestyle changes. These “home remedies” are typically suggested before the use of medication.
HOME REMEDY
Certain home remedies or lifestyle changes may help to relieve your IBS symptoms without the use of medication. Examples of these lifestyle changes include:
– regular physical exercise
– cutting back on caffeinated beverages that stimulate the intestines
– eating smaller meals
– minimizing stress (talk therapy may help)
– taking probiotics (“good” bacteria normally found in the intestines) to help relieve gas and bloating
– avoiding deep-fried or spicy foods
MEDICAL TREATMENT OPTION
– Alosetron (LOTRONEX) is intended for use only in women with severe cases of IBS-D who haven’t responded to other treatments
– Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) (eg, amitriptyline [Elavil]) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
– Antibiotics such as rifaximin (Xifaxan), which stays in the gut without being reabsorbed, may benefit patients with IBS symptoms caused by SIBO(small intestine bacterial overgrowth.
DIETARY INTERVENTIONS
Just as there is no single therapy for treating IBS, it’s important to remember there’s no single dietary strategy either.
– Avoid or minimize high-gas foods such as broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and beans as well as carbonated beverages.
– Avoid chewing gum or drinking liquids through a straw, both of which can lead to swallowing air, which causes more gas.
– Minimize consumption of fried or other high-fat foods.
– Avoid consuming large meals, which may promote cramping and/or diarrhea, and consume smaller, more frequent meals instead.
– Minimize consumption of foods high in lactose, such as milk, ice cream, and soft cheeses, especially if lactose intolerance is suspected. Hard cheeses, lactose-free milk, lactose-free ice cream, and low-lactose or lactose-free yogurt or kefir, which either have no lactose or tend to be lower in lactose than other dairy products, may be more easily tolerated.
– Drink adequate amounts of fluid to help alleviate constipation.
– Avoid or minimize alcohol and caffeine intake, especially with IBS-D, as both substances can stimulate the intestines and lead to diarrhea.
– Avoid artificial sweeteners that contain sugar alcohols, such as sorbitol, mannitol, and xylitol, which may cause diarrhea.
– Consume foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oatmeal, oat bran, oranges, strawberries, nuts, and carrots.
It’s important to note that while foods with soluble fiber may be beneficial for IBS patients, foods high in insoluble fiber, such as whole wheat, wheat bran, raisins, and corn bran, may further aggravate IBS symptoms in certain individuals
In addition, some IBS patients may not be able to tolerate other sources of soluble fiber, such as lentils, apples, pears, and beans, because they’re sources of fermentable carbohydrates
THE LOW FODMAP DIET
The low-FODMAP elimination diet is based on limiting certain short-chain carbohydrate-containing foods, including sugars, starches, and fibers that some people can’t fully digest and absorb.
These dietary carbohydrates are lactose, fructose, fructans, polyols, and galactans/galacto-oligosaccharides and are found in certain grains, fruits, vegetables, dried peas and beans, milk products, and prepared foods and beverages.
HIGH FODMAP CARBS HIGH FODMAP FOODS
Lactose Dairy and its products
Fructose Apples, pear, mango, watermelon
Fructans Garlic, artichokes, wheat, beer
polyols Cherries, apricots, peaches, sorbitol, xylitol
Galacto-oligosaccharrides Beans, cabbage, lentils, soy products
SOURCES:
1. https://www.healthline.com/health/irritable-bowel-syndrome#ibs-with-stress
2. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langas/article/PIIS2468-1253(20)30217-X/fulltext#:~:text=Our%20data%20therefore%20suggest%20that,criteria%20and%20methodology%20were%20pooled.
3. https://www.bcdietitians.ca/blog/what-is-irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs-and-how-to-improve-your-gut-health


 Have you ever had a disruption in your bowels after taking a food you knew you shouldn’t have?
Have you ever had a disruption in your bowels after taking a food you knew you shouldn’t have? 

